Adversarial Experts Model for Black-box Domain Adaptation
Siying Xiao, Mao Ye, Qichen He, Shuaifeng Li, Song Tang, Xiatian Zhu
Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACM MM)
Published:
Key Words: Black-box Domain Adaptation; CLIP; Adversarial Experts
Abstract
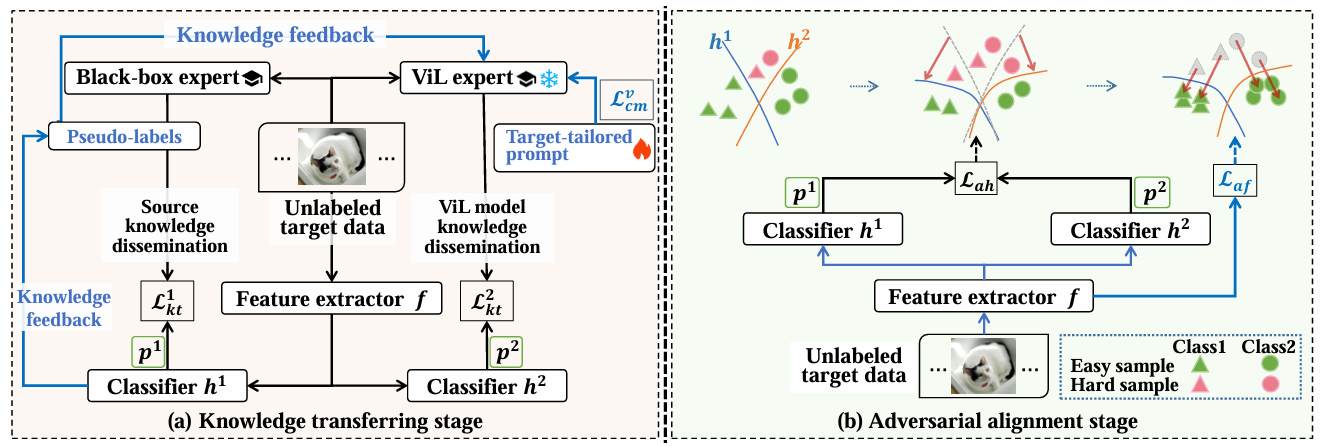
Black-box domain adaptation treats the source domain model as a black box. During the transfer process, the only available information about the target domain is the noisy labels output by the black-box model. This poses significant challenges for domain adaptation. Conventional approaches typically tackle the black-box noisy label problem from two aspects: self-knowledge distillation and pseudo-label denoising, both achieving limited performance due to limited knowledge information. To mitigate this issue, we explore the potential of off-the-shelf vision-language (ViL) multimodal models with rich semantic information for black-box domain adaptation by introducing an Adversarial Experts Model (AEM). Specifically, our target domain model is designed as one feature extractor and two classifiers, trained over two stages: In the knowledge transferring stage, with a shared feature extractor, the black-box source model and the ViL model act as two distinct experts for joint knowledge contribution, guiding the learning of one classifier each. While contributing their respective knowledge, the experts are also updated due to their own limitation and bias. In the adversarial alignment stage, to further distill expert knowledge to the target domain model, adversarial learning is conducted between the feature extractor and the two classifiers. A new consistency-max loss function is proposed to measure two classifier consistency and further improve classifier prediction certainty. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. Code is available at https://github.com/singinger/AEM.
Cite this paper
@inproceedings{10.1145/3664647.3681123,
author = {Xiao, Siying and Ye, Mao and He, Qichen and Li, Shuaifeng and Tang, Song and Zhu, Xiatian},
title = {Adversarial Experts Model for Black-box Domain Adaptation},
year = {2024},
isbn = {9798400706868},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3664647.3681123},
doi = {10.1145/3664647.3681123},
abstract = {Black-box domain adaptation treats the source domain model as a black box. During the transfer process, the only available information about the target domain is the noisy labels output by the black-box model. This poses significant challenges for domain adaptation. Conventional approaches typically tackle the black-box noisy label problem from two aspects: self-knowledge distillation and pseudo-label denoising, both achieving limited performance due to limited knowledge information. To mitigate this issue, we explore the potential of off-the-shelf vision-language (ViL) multimodal models with rich semantic information for black-box domain adaptation by introducing an Adversarial Experts Model (AEM). Specifically, our target domain model is designed as one feature extractor and two classifiers, trained over two stages: In the knowledge transferring stage, with a shared feature extractor, the black-box source model and the ViL model act as two distinct experts for joint knowledge contribution, guiding the learning of one classifier each. While contributing their respective knowledge, the experts are also updated due to their own limitation and bias. In the adversarial alignment stage, to further distill expert knowledge to the target domain model, adversarial learning is conducted between the feature extractor and the two classifiers. A new consistency-max loss function is proposed to measure two classifier consistency and further improve classifier prediction certainty. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. Code is available at https://github.com/singinger/AEM.},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia},
pages = {8982–8991},
numpages = {10},
keywords = {adversarial learning, black-box domain adaptation, vision-language model},
location = {Melbourne VIC, Australia},
series = {MM '24}
}